Addition reaction
Addition reaction are those in which atoms or groups of atoms are simply added to a double or triple bond without the elimination of any atom or other molecules.
In these reactions, at least one π bond is lost while two new σ bonds are formed.
Double bonds become saturated, and triple bonds are converted into double bonds or may become saturated by further addition.
Halogenation
Hydration
Hydrogenation
Mechanism of Addition Reaction [Electrophilic]
Mechanism of Addition Reaction [Nucleophilic]
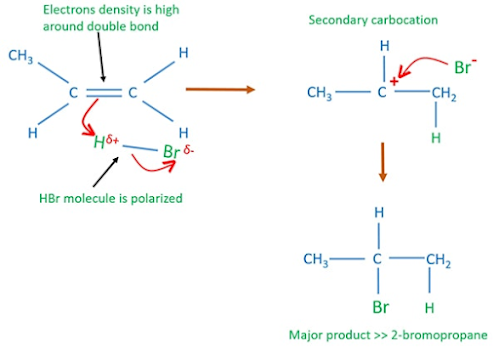
What happens when propene is treated with hydrogen bromide?
Propene reacts with HBr and produce CH3CHBrCH3 [2-bromopropane].
It is an alkyl halide compound and this is an addition reaction.
Also you can treat HBr in the presence of organic peroxides to change the location of where bromine atom is joint.
Reaction of propene and HBr belongs to the nucleophilic addition reaction type.
Mechanism of HBr addition of propene
HBr molecule is polarized because there is a electronegatively difference between hydrogen and bromine atoms. Also, electrons density of double bond is higher in alkene.
1.Electrophile (H+ ion) attacks the propene molecule and has the possibility to form two carbocations. Secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation. Therefore, the attack of electrophile (H+ ion) on propene results in the formation of more stable secondary carbocation.
2. Then formed bromide ion reacts with the carbocation carbon to form the final product.
The electrophilic addition of HBr to an unsymmetrical alkene always occurs via the most stable carbocation formation and it is indirectly expressed in Markovnikov's rule.










No comments:
Post a Comment